Amyloid‑β–Degrading Enzymes Derived from Habu Snake Venom
A Highly Selective Amyloid‑β Degrader as a Seed for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics
Overview
Current Alzheimer’s disease therapies provide only limited cognitive benefit, and there is an unmet need for disease‑modifying drugs that directly reduce amyloid‑β (Aβ) accumulation.
The inventors identified habu snake (Protobothrops flavoviridis) venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs), evolutionarily related to non‑amyloidogenic APP‑processing ADAM proteases, as potent Aβ‑degrading enzymes.
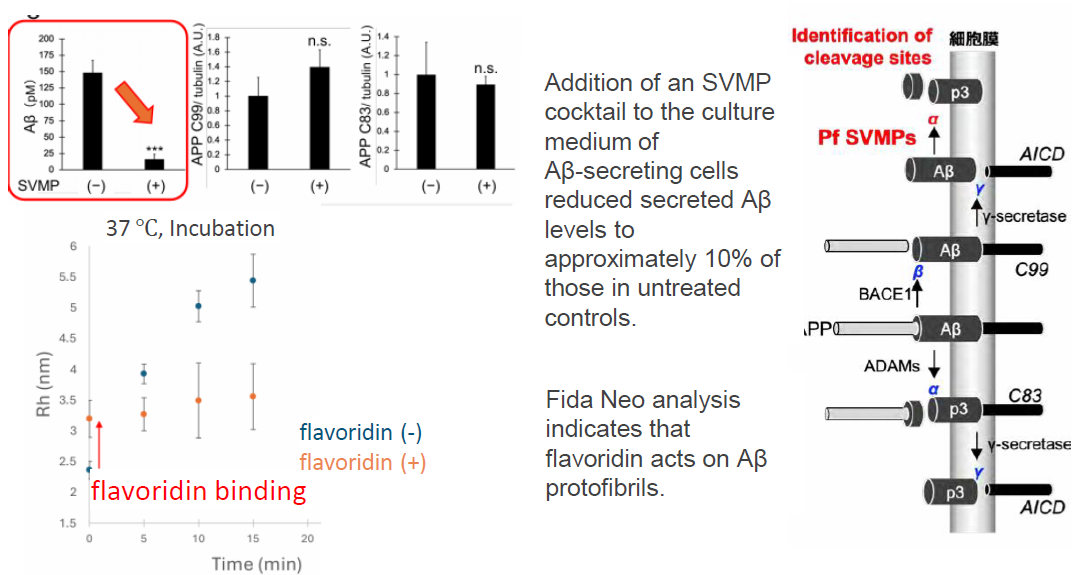
In vitro, an SVMP cocktail cleaved secreted Aβ at the APP α‑cleavage–equivalent site, converted it to non‑toxic p3 fragments, and reduced Aβ levels in culture medium by about 90%.
Among these, the flavoridin‑precursor–derived SVMP targets both monomeric and aggregated Aβ and shows higher substrate selectivity than neprilysin with minimal neuropeptide degradation, supporting its potential as a low‑toxicity, disease‑modifying AD drug lead.
Key Points
・Selective α‑site cleavage
・Bypasses endogenous inhibition
・High substrate specificity
・High‑efficiency Aβ clearance
・Suppression of fibril formation
Features・Outstandings
Product Application
・A gene therapy product that employs an AAV vector to drive sustained brain expression of the flavoridin precursor gene and thereby promote Aβ degradation.
Related Works
IP Data
IP No. : WO2025/100469
Inventor : E. Futai, T. Ogawa, H. Kawasaki, S. Sato, M.Hidaka
keyword : Therapeutics, Dementia, Aβ, Alzheimer'sdisease, Venomics
