Quantum bit / Quantum sensor material using SiO2
Can be produced at low cost. Proven write operation.
Overview
Nitrogen-vacancy center (NV center) in diamond satisfies the characteristics required for qubits, and expected to be applied to quantum computers and quantum sensors. Other candidate materials are divacancy centers (VV centers) in SiC and Ce-implanted Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG). However, the problem with all of these materials is the high cost of raw materials, and it is expected to be difficult to scale up.
The present invention demonstrates that light emitting centers (Ce3+) can be formed in Ce implanted SiO2 or MgAl2O4
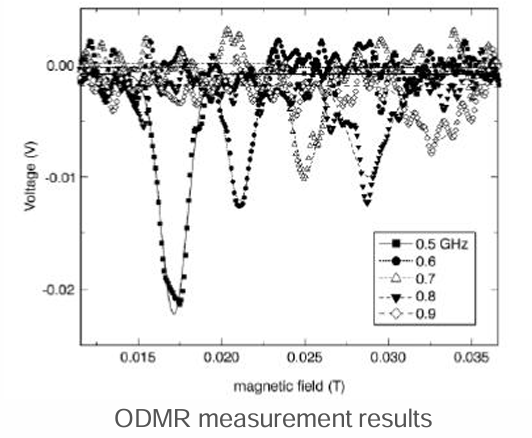
substrates. Optically Detected Magnetic Resonance (ODMR) measurements demonstrate the feasibility of write operations in quantum dots. It is possible to realize a quantum bit / quantum sensor at low cost.
Write operations in quantum dots
Product Application
・Quantum sensors such as ODMR
・Quantum bits for quantum computers
Related Works
[1] Manato Kawahara et al, Applied Physics Express 17, 072004 (2024)
https://doi.org/10.35848/1882-0786/ad59f4
IP Data
IP No. : WO 20252/047531 A1
Inventor : KANAI Shun, ABE Yuichiro, KAWAHARA Manato, FUKAMI Shunsuke, OHNO Hideo, ISHIHARA Jun, KODA Makoto, TAKANO Koki
keyword : quantum bit, quantum sensor, NV center, nitrogen vacancy center, light emission center, quantum computer, ODMR
