A Nonvolatile Register with a Reference Load Sharing Scheme
Reduction in power consumption and area by minimizing the number of MTJ devices
Overview
Intermittent computing executes tasks as energy accumulates,
enabling continuous edge computing under unstable, low-power
energy harvesting conditions. Ensuring processing continuity
before and after frequent power interruptions is essential. A
nonvolatile logic circuit using nonvolatile registers allows internal
state retention with only local data transfers, making it a
promising option.
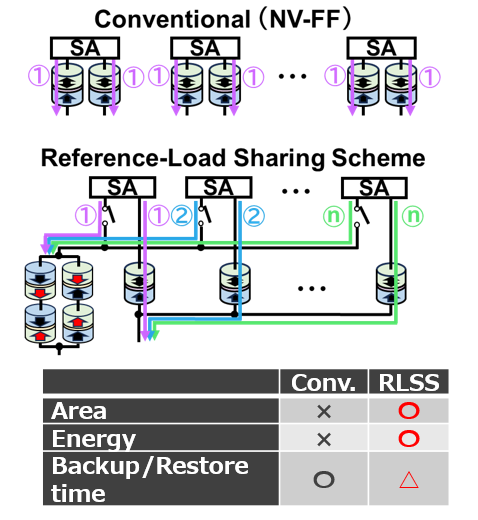
Conventional nonvolatile registers connect 1-bit memory circuits
(nonvolatile flip-flops, NV-FFs) per bit, requiring two MTJ devices
per bit, leading to significant area and energy overhead. This
invention proposes the Reference-Load Sharing Scheme (RLSS),
where 1-bit information is retained between an MTJ device and a
reference MTJ device using a sequential backup-restore process.
This reduces MTJ device count, shares circuit functions, and
achieves 49% lower energy consumption and 34% area
reduction, as confirmed by simulations.
Backup and Restore Operation and Performance Comparison
Product Application
・Nonvolatile registers and nonvolatile flip-flops
・Intermittent computing and energy harvesting
・Reduction in power consumption of existing desktop and supercomputers
Related Works
[1] DOI: 10.1109/MWSCAS60917.2024.10658712
IP Data
IP No. : JP2024-220627
Inventor : NATSUI Masanori, YOSHIDA Tomoo, HANYU Takahiro
keyword : Nonvolatile registers, Nonvolatile flip-flops, Intermittent computing, Energy harvesting, Reduction in power consumption
